Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived Exosome Research and Application
The development and study of the Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosome has facilitated an in-depth understanding of the mechanisms of infection and transmission of pathogens and has also opened up new possibilities for the development of safe and effective cell-free vaccine strategies. Creative Biolabs specializes in advancing the understanding of the Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosome by providing a comprehensive range of research services from isolation to analysis.
Isolation of Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived Exosome
-
Culture Streptococcus pneumoniae overnight at 37°C and then collect the bacterial medium.
-
Centrifuge Streptococcus pneumoniae cultures at low speed to remove bacterial bodies and debris.
-
Aseptically filter the Streptococcus pneumoniae supernatant and confirm the sterility of the supernatant by overnight incubation.
-
Ultracentrifuge the sterile supernatant to obtain exosome precipitates.
-
Resuspend the Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosomes with PBS.
-
Further purify Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosome from soluble protein impurities using SEC columns loaded with agarose.
Research on Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived Exosome
|
Research
|
Conclusion
|
|
Characterization of vesicles isolated from Streptococcus pneumoniae.
|
Cryo-transmission electron microscopy observations revealed that vesicles from Streptococcus pneumoniae display heterogeneity in morphology, size, and content, identified to a variety of structures and particle diameters including spherical, rod-shaped, chain-like arrangements and irregularities. In addition, there may be different shades of color depending on the content.
|
|
Cytotoxicity of Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosome.
|
Cell viability assays revealed that the human lung epithelial cell line, human keratinocyte-forming cell line, differentiated human macrophage phenotype, and mouse dendritic cell line exhibited tolerance to Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosome without any toxic effects.
|
|
Cellular Uptake of Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosome.
|
Flow cytometry and fluorescent tracer exosome assays revealed that Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosome could be taken up by human lung epithelial cell lines, human keratinocyte-forming cell lines, differentiated human macrophage phenotypes, and mouse dendritic cell lines for the delivery of bacterial-associated cargoes, and the extent of uptake was better in immune cells.
|
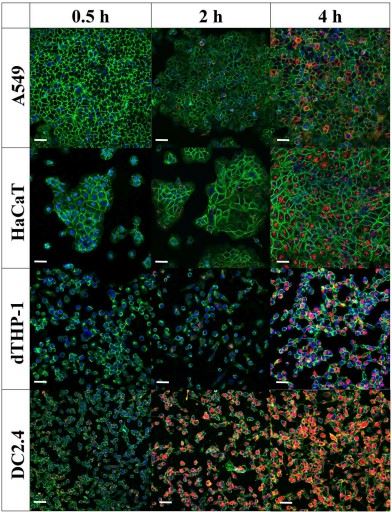 Fig. 1 Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosomes are taken up by cells in a time-dependent manner.1
Fig. 1 Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosomes are taken up by cells in a time-dependent manner.1
|
Research
|
Conclusion
|
|
The immunostimulatory potential of Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosome.
|
-
ELISA of dendritic cells after incubation with exosomes revealed that Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosomes were able to stimulate the release of inflammation-associated factors, showing potential to stimulate immunity.
-
Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosomes were able to activate NF-κB signaling in macrophages in a dose-dependent manner.
|
|
Biological functions of immunity induced by Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosomes and their mechanisms.
|
Examination of PBMC cells and spleens from mice injected intravenously with exosomes revealed that Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosome induced a significant increase in M2 macrophages and immune responses.
The contribution of bacterial lipoproteins to the activation of NF-κB and regulation of host immune signaling by the Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosome was shown by comparison with exosomes derived from the same strain with gene deletion mutations.
|
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosomes regulation of adaptive immunity.
|
-
Analysis of the Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosome-treated mouse models revealed that topical inoculation with Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosome triggered the recruitment of host immune cells in the microenvironment and immune responses.
-
In addition, Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosome induced the activation of M2-type macrophages thereby favoring the chronic carriage of bacteria.
|
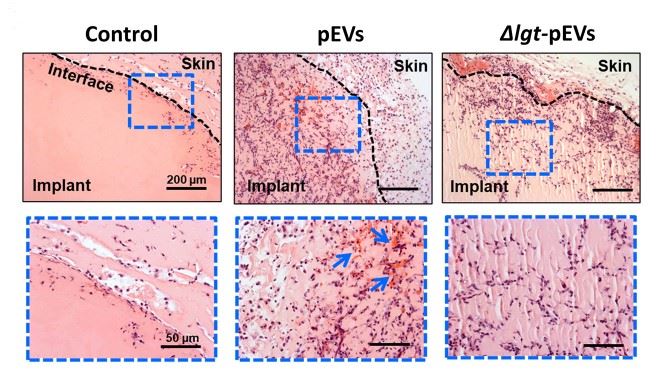 Fig. 2 Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosomes induced host cell recruitment.2
Fig. 2 Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosomes induced host cell recruitment.2
Recently there has been a growing understanding of exosome-like vesicles isolated from Gram-positive bacteria including Streptococcus pneumoniae. Creative Biolabs can provide efficient and reliable services for the study of Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosomes, contributing to the exploration of bacterial vesicles as vaccine candidates. Please contact us with interest.
References
-
Mehanny, Mina, et al. "Streptococcal extracellular membrane vesicles are rapidly internalized by immune cells and alter their cytokine release." Frontiers in immunology 11 (2020): 80.
-
Yerneni, Saigopalakrishna S., et al. "Pneumococcal extracellular vesicles modulate host immunity." MBio 12.4 (2021): 10-1128.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosomes are taken up by cells in a time-dependent manner.1
Fig. 1 Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosomes are taken up by cells in a time-dependent manner.1
 Fig. 2 Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosomes induced host cell recruitment.2
Fig. 2 Streptococcus pneumoniae-derived exosomes induced host cell recruitment.2








