Lactobacillus acidophilus-derived Exosome Research and Application
Lactobacillus acidophilus is a lactic acid bacterium belonging to the Lactobacillus genus within the Lactobacillaceae family. This microbial strain has been extensively studied and valued in the field of biomedical research due to its probiotic effects in the human intestinal tract. Abundant research on Lactobacillus acidophilus suggests that it holds significant potential in improving gut health and enhancing the overall immune system. As a small microbial product, exosomes derived from Lactobacillus acidophilus are rich in bioactive molecules. Do these molecules have medical application prospects? Creative Biolabs is here to introduce Lactobacillus acidophilus-derived exosome research to support innovative ideas from our clients.
Lactobacillus acidophilus as a Beneficial Probiotic
Lactobacillus acidophilus plays multiple crucial roles in the human body, including but not limited to:
-
Regulating Gut Microbiota Imbalance: Lactobacillus acidophilus helps maintain a healthy composition of gut microbiota by interacting with intestinal mucosal cells, forming a biological barrier, and adjusting interactions with other bacteria. This assists in inhibiting the growth and invasion of pathogenic bacteria.
-
Improving Lactose Intolerance: It secretes lactase, aiding in the breakdown and absorption of lactose, thereby alleviating symptoms of lactose intolerance.
-
Nutritional Benefits: The fermentation process of Lactobacillus acidophilus produces lactic acid, which enhances the absorption of minerals such as calcium, phosphorus, and iron. It also produces B-vitamins, beneficial for the development of nerve cells.
-
Enhancing Immunity: Colonizing the intestinal tract, Lactobacillus acidophilus can activate the body's immune system, boosting its infection-fighting abilities. It may also help inhibit the formation and proliferation of cancer cells.
-
Slowing Aging: Metabolites of Lactobacillus acidophilus, like lactic acid, can inhibit the production of harmful metabolites, contributing to a slowing of the body's aging process.
In the medical field, Lactobacillus acidophilus has been extensively researched and applied with potential applications, particularly in the following areas:
-
Helicobacter pylori-Related Gastritis: Helicobacter pylori infection is a major cause of chronic gastritis, and Lactobacillus acidophilus can assist in eradicating Helicobacter pylori, enhancing the effectiveness of gastritis treatment.
-
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea: Lactobacillus acidophilus can prevent and treat antibiotic-associated diarrhea, especially with significant effects in children.
-
Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Probiotic preparations, including Lactobacillus acidophilus, can alleviate symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome, improving their quality of life.
-
Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Lactobacillus acidophilus has shown some effectiveness in the treatment of ulcerative colitis and holds potential in treating inflammatory bowel disease, although more research is needed to determine the optimal application methods.
Research on Lactobacillus acidophilus-derived Exosomes
|
|
Extraction Method
|
Research Methods
|
Research Findings
|
Representative Figures
|
|
1
|
Ultracentrifugation
|
Nanoparticle Tracking and Analysis; Atomic Force Microscopy observation; Protein blotting hybridization analysis; Proteomic analysis
|
Lactobacillus acidophilus-derived exosomes are enriched with proteins related to antimicrobial peptide production and signal transduction, which may be significant for intercellular communication in Lactobacillus acidophilus and their roles in microbial communities.
|
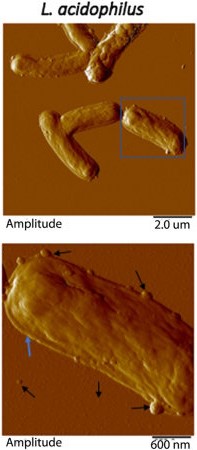
Fig.1 Representative atomic force microscopy amplitude images of Lactobacillus acidophilus and their exosomes.1,3
|
|
2
|
Ultracentrifugation
|
Comparative genomics analysis; Proteomic analysis; Growth inhibition and pore formation experiments; Membrane fusion experiments
|
Lactobacillus acidophilus-derived exosomes are rich in proteins related to bacteriocin-coding genes. These exosomes can inhibit the growth of Lactobacillus delbrueckii by fusing with the cell membrane of Lactobacillus delbrueckii, transferring their contents inside and inhibiting its growth.
|
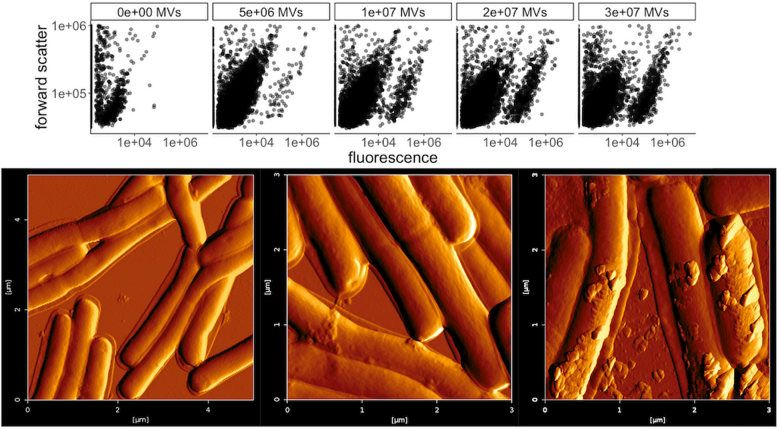
Fig.2 Membrane fusion of exosomes.2,3
|
Exosomes, as an important field of research in the microbial realm, hold broad prospects for biological and medical applications. Building upon years of biotechnology experience and specialized knowledge, Creative Biolabs offers high-quality microbial-derived exosome extraction and research services, providing comprehensive solutions to our clients. If you have any needs or questions regarding these services, please feel free to contact us.
Bacteria-derived Exosome Isolation and Identification
In Vitro Functional Discovery of Bacteria-derived Exosomes
In Vivo Functional Discovery of Bacteria-derived Exosomes
References
-
Dean, SN.; et al. Isolation and characterization of Lactobacillus-derived membrane vesicles. Scientific Reports. 2019, 9(1):877.
-
Dean, SN.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus membrane vesicles as a vehicle of bacteriocin delivery. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2020, 11:710.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:











