Staphylococcus aureus-derived Exosome Research and Application
Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive bacterium that has garnered significant attention in the field of biomedicine. This bacterium is a member of the normal flora on human skin and mucous membranes but can also cause various infections, including skin infections, respiratory tract infections, bloodstream infections, and even severe hospital-acquired infections. The mechanism by which Staphylococcus aureus triggers infections is closely associated with the molecular factors it produces. In recent years, researchers have discovered that Staphylococcus aureus can produce small vesicles called "exosomes" or extracellular vesicles. These vesicles contain a variety of biomolecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. Creative Biolabs focuses on the research outcomes and potential applications of exosomes derived from Staphylococcus aureus.
Research Motivation of Exosomes Derived from Staphylococcus aureus
-
Understanding the infection mechanism: Staphylococcus aureus is a common pathogen, and studying its exosomes helps to gain deeper insights into the infection mechanism. The molecular factors within exosomes can reveal how Staphylococcus aureus interacts with host cells, invades the host, and triggers infections.
-
Clinical Applications: Research on exosomes derived from Staphylococcus aureus offers new approaches and potential applications to improve the treatment and management of infections and related diseases. Exosome research has the potential to bring innovation to the field of clinical medicine, enhancing treatment efficiency and the success rate of vaccine development.
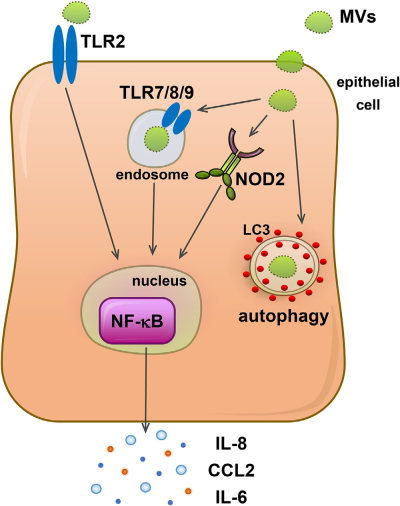 Fig.1 Model of immune detection, inflammatory signaling and intracellular fate of Staphylococcus aureus membrane vesicles.1,3
Fig.1 Model of immune detection, inflammatory signaling and intracellular fate of Staphylococcus aureus membrane vesicles.1,3
Current Potential of Exosomes Derived from Staphylococcus aureus
-
Vaccine Development: Exosomes derived from Staphylococcus aureus naturally carry antigenic molecules. Studies have shown that exosomes purified from clinically isolated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus can stimulate proinflammatory cytokines in mouse spleen cells through interaction with Toll-like receptors. Furthermore, total immunoglobulin E in mouse serum significantly increases after a second administration, indicating that exosomes derived from Staphylococcus aureus naturally carry antigenic molecules. Through genetic engineering, these exosomes can be engineered into vaccine carriers. Such vaccines can be used to prevent Staphylococcus aureus infections, eliciting specific antibody and cellular immune responses, enhancing the immune system's defense against the bacteria, and reducing the risk of infection.
-
Drug Delivery: Exosomes derived from Staphylococcus aureus have effective biomolecules on their surface, and their lipid bilayer structure makes them excellent drug carriers. Research has shown that nanoparticles enveloped by the membrane structure of these exosomes have the capability for active targeted delivery in vitro and in vivo. By loading antibiotics, these nanoparticles significantly eliminate Staphylococcus aureus. In the future, it is believed that through endogenous modification or loading with exogenous drugs, they can encapsulate and deliver drugs to infection sites or specific tissues, enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of drugs. This holds immense potential for treating Staphylococcus aureus infections and other diseases.
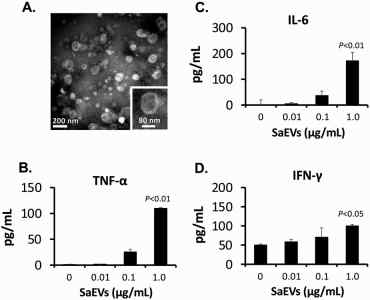 Fig.2 Stimulation of proinflammatory cytokines from naïve mouse spleen cells by extracellular vesicles from Staphylococcus aureus.2,3
Fig.2 Stimulation of proinflammatory cytokines from naïve mouse spleen cells by extracellular vesicles from Staphylococcus aureus.2,3
Based on the research on exosomes derived from Staphylococcus aureus, we believe that there is a wealth of untapped information and potential in the field of treating Staphylococcus aureus infections. Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive services for microbial-derived exosome research. If clients are interested in exploring these naturally antigen-carrying nanoparticles, please feel free to contact us.
Bacteria-derived Exosome Isolation and Identification
In Vitro Functional Discovery of Bacteria-derived Exosomes
In Vivo Functional Discovery of Bacteria-derived Exosomes
References
-
Bitto, NJ.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus membrane vesicles contain immunostimulatory DNA, RNA and peptidoglycan that activate innate immune receptors and induce autophagy. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 2021, 10(6):e12080.
-
Asano, K.; et al. Extracellular vesicles from methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus stimulate proinflammatory cytokine production and trigger IgE-mediated hypersensitivity. Emerging Microbes & Infections. 2021, 10(1):2000-2009.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Model of immune detection, inflammatory signaling and intracellular fate of Staphylococcus aureus membrane vesicles.1,3
Fig.1 Model of immune detection, inflammatory signaling and intracellular fate of Staphylococcus aureus membrane vesicles.1,3
 Fig.2 Stimulation of proinflammatory cytokines from naïve mouse spleen cells by extracellular vesicles from Staphylococcus aureus.2,3
Fig.2 Stimulation of proinflammatory cytokines from naïve mouse spleen cells by extracellular vesicles from Staphylococcus aureus.2,3








