Quantitative Monosaccharaide Analysis Service
Services Published Data FAQs Customer Review
High-level Monosaccharide Quantitative Analysis Service at Creative Biolabs
Abnormal glycosylation is related to many types of cancer. Cancer cells will gradually release proteins with abnormal glycosylation on their surface into body fluids. Therefore, the monosaccharide analysis in liquid-like molecules helps reveal changes in glycosylation, thereby discovering candidate biomarkers associated with disease. Creative Biolabs has a powerful Glycoprotein Analysis Platform and technical teams, and we provide high-quality monosaccharide quantitative analysis services to clients around the world. Quantitative analysis of monosaccharides in glycoproteins is of great significance for understanding the structure and functions of glycoproteins, ensuring quality control, disease diagnosis, and biomarker research.
Quantitative analysis of monosaccharides in glycoproteins typically requires the following steps:
-
Release of monosaccharides
We use appropriate glycosidase (e.g. β-mannosidase, α-galactosidase, etc.) or PNGase F to hydrolyze glycoproteins. These enzymes cleave the sugar group's linkage to the protein, releasing the monosaccharides and protein moieties. In addition, under acidic conditions, sugar groups in glycoproteins are also released by hydrolysis, depending on the acidolysis conditions used.
-
Derivatization of monosaccharides
To increase the detection sensitivity and selectivity of monosaccharides, we often need to derivatize monosaccharides, such as acetylation.
-
Separation and detection of monosaccharides
We use a variety of techniques to separate various monosaccharides and conduct quantitative analysis of the separated monosaccharides. We have developed different analytical methods to efficiently and accurately determine the monosaccharide composition in glycoproteins. Commonly used detection methods include but are not limited to the following.
-
We combine high-performance anion exchange chromatography with a pulsed amperometric detector (HPAEC-PAD), which is a simple and convenient method that analyzes the monosaccharide composition in glycoproteins sensitively and quickly without the need for pre-column or post-column solute derivatization.
-
We use high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection (HPLC-FL) to analyze monosaccharides in glycoproteins. We select 2-aminobenzoic acid (2-AA) and 2-aminobenzamide (2-AB) as fluorescent labels, which are highly fluorescent and reactive, and the detection of monosaccharides is achieved by labeling carbohydrates with reducing ends before the column.
-
We also couple HPLC with mass spectrometry to achieve monosaccharide analysis in glycoproteins. Commonly used ionization methods include electrospray ionization (ESI) or chemical ionization (CI). We use the mass spectrometry data collected by the mass spectrometer to confirm and quantify the monosaccharides in the sample.
-
In addition, laser-induced fluorescence capillary electrophoresis (CE-LIF) technology also realizes monosaccharide analysis in glycoproteins. We use a laser to excite a fluorescent dye (usually a fluorescent probe that labels the monosaccharide) in the monosaccharide molecule, causing it to emit a fluorescent signal at a specific wavelength. The fluorescence signal is then captured and recorded by a detector to achieve an accurate analysis of monosaccharides in glycoproteins.
Quantitative analysis of monosaccharides in glycoproteins is a complex process. We combine a variety of technical means and analytical methods to ensure accurate determination of the content and composition of monosaccharides. In addition, we offer a variety of analytical services such as Sialic Acid Analysis, Sugar Nucleotide Analysis, and Glycosaminoglycan Analysis services.
 Fig.1 Detailed steps for quantitative analysis of monosaccharides.
Fig.1 Detailed steps for quantitative analysis of monosaccharides.
Published data
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is a very effective separation technique in carbohydrate analysis. In this study, the authors developed a simple and efficient sugar labeling method using iodine as a catalyst and analyzed various monosaccharide components using CE. The authors used 2,3-naphthalene diamine to derivatize the D- and L-enantiomers of 11 common monosaccharides (e.g., glucose, fucose, rhamnose, mannose, etc.) to generate the corresponding D- and L-aldehyde-naphthylimidazole (NAIM) derivatives. Subsequently, a simple gross CE method was established to analyze the composition and configuration of sugars by measuring the migration time of these derivatives in a high pH borate buffer. The quantitative range of this method was 10 to 500 ppm, and the limit of detection (LOD) was 1 ppm. The results showed that aldehyde-NAIM derivatives, as an effective reagent, could analyze the composition and configuration of sugars using CE technology, showing good linearity and a short analysis time.
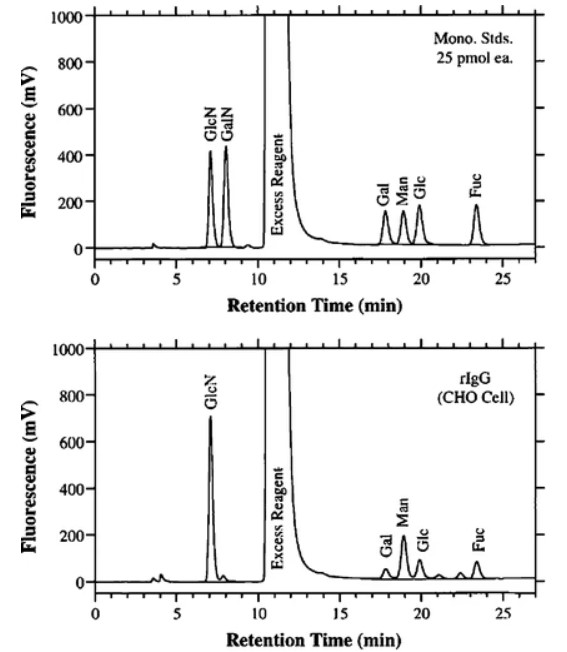 Fig.2 Electropherogram of monosaccharides derivatized with 2,3-naphthalenediamine.1
Fig.2 Electropherogram of monosaccharides derivatized with 2,3-naphthalenediamine.1
Advantages
-
High sensitivity: We provide low-concentration monosaccharide detection services.
-
High accuracy: We provide precise monosaccharide content analysis results.
-
High reliability: Our analytical data is highly reproducible.
-
Diversity: We provide monosaccharide analysis for various types of glycoproteins.
Application
-
Food industry: Monosaccharide analysis is used to detect the content of glucose, fructose, and other monosaccharides in food, thereby guiding food processing and adjusting product taste.
-
Biomedicine: Monosaccharides are components of cell surface sugar groups and are related to key biological processes such as cell-cell interactions and signal transduction. Monosaccharide analysis can understand the composition and changes of sugar groups on the cell surface, which helps study the mechanisms of disease.
-
Environmental monitoring: Monosaccharide analysis is used to monitor microbial activities in water, soil, and other environments to provide data support for environmental pollution monitoring.
Creative Biolabs has extensive experience in monosaccharide analysis and can provide personalized monosaccharide analysis services according to client needs. In addition, we provide clients with comprehensive data analysis and result interpretation. Please do not hesitate to contact us if you would like to acquire detailed service.
FAQ
Q1: What is monosaccharide analysis and why is it important?
A1: Monosaccharide analysis is the process of quantitatively and qualitatively identifying the monosaccharide components of carbohydrate molecules. It is of great significance in fields such as biomedical research, the food industry, and environmental monitoring, and helps identify disease-related biomarkers, monitor food ingredients, and evaluate microbial activities.
Q2: Why do we need to derivatize monosaccharides?
A2: In monosaccharide analysis, the main purpose of derivatization is to improve the sensitivity and selectivity of detection. By derivatizing monosaccharides, such as acetylation or other chemical modifications, their fluorescence or mass spectrometry signals can be significantly enhanced, so that low concentrations of monosaccharides are accurately detected and quantified. In addition, derivatization improves separation effects, reduces background interference, and improves the reliability of analysis results. These advantages make derivatization an indispensable and important step in monosaccharide analysis.
Q3: What types of samples can you perform monosaccharide analysis on? How to analyze?
A3: Monosaccharide analysis is applied to many types of samples, including biological fluids (such as serum, and urine), cell culture fluids, tissue extracts, etc. We use specific enzymes (such as PNGase F) to hydrolyze glycoproteins to release the monosaccharides. The released monosaccharides are then derivatized to improve the detection sensitivity and accurately determine the composition and content of monosaccharides in the sample.
Customer Review
Highly Sensitive Detection
“We obtained significant monosaccharide detection results even in low-concentration samples, which was particularly important for our study of changes in cell surface glycosylation. We were very grateful to Creative Biolabs for its high-sensitivity analysis.”
Continuous Follow-up Support
“During the entire analysis process, Creative Biolabs' technical team showed a high degree of professionalism and dedication, answering our questions at any time, which made us feel at ease. Even after the analysis was completed, Creative Biolabs still kept in touch to provide follow-up technical support and suggestions, demonstrating their consistent service spirit.”
Reference
-
Lin, Chunchi, et al. "Monosaccharide-NAIM derivatives for D-, L-configurational analysis." Molecules 16.1 (2011): 652-664. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Detailed steps for quantitative analysis of monosaccharides.
Fig.1 Detailed steps for quantitative analysis of monosaccharides.
 Fig.2 Electropherogram of monosaccharides derivatized with 2,3-naphthalenediamine.1
Fig.2 Electropherogram of monosaccharides derivatized with 2,3-naphthalenediamine.1

