N-Linked Glycoengineering Service in Mammalian Cell
N-glycan attachments are crucial in many therapeutic glycoproteins, and altering the glycan composition can significantly impact the efficacy of biotherapeutics. Due to the subtle variations of glycan structures in human and non-human mammalian cells, such as the widely used CHO cells, therapeutic glycoproteins produced in native CHO cells may have limited efficacy. Consequently, multiple glycoengineering strategies and advanced tools and technologies have been employed to tailor the glycosylation structures generated by nonhuman mammalian cells.
Constraints of Glycoproteins Produced in Non-human Mammalian Cells
Immunogenic epitopes like α1, 3 Gal and Neu5Gc.
Non-human mammalian cell lines synthesize additional carbohydrate epitopes including the α1,3 Gal and Neu5Gc, exerting safety concerns and short half-lives to therapeutic glycoproteins.
Presence of α1,6-fucosylation.
Antibodies produced in CHO cells often exhibit a substantial level of α1,6-fucosylation catalyzed by FUT8, which reduces ADCC and, consequently, hinders its therapeutic efficacy.
Absence of α2,6-sialylation.
Recombinant proteins produced in CHO cells display α2,3-linked terminal sialic acid only. The absence of terminal sialylation impacts protein properties including biological activity and in vivo circulatory half-life.
Absence of bisecting GlcNAc.
CHO cells typically do not express GnTIII, resulting in the absence of bisecting GlcNAc residues in their glycoforms. This absence can impact the efficacy of antibodies.
Heterogeneous glycans
The heterogeneity can be attributed to microheterogeneity and macroheterogeneity, posing challenges to product consistency and having adverse effects on drug potency and pharmacokinetics.
N-Linked Glycoengineering Services in Mammalian Cell at Creative Biolabs
With extensive experience in Glycoengineering Services and access to cutting-edge technologies, Creative Biolabs has made considerable efforts to overcome these limitations associated with glycoproteins produced in mammalian cells and yielded successful outcomes in engineering mammalian cell lines for the production of human therapeutic glycoproteins. We are excited to develop N-linked glycoengineering services with various strategies, especially Genetic Engineering. We utilize a variety of combinatorial approaches including knockdown or knockout of enzymes such as sialidase or fucosyltransferase, and transient expression or knockin of glycosylation enzymes to address multiple bottlenecks in glycoengineering processes. Through a combination of gene knockout and knockin, we have successfully obtained therapeutic rhEPO with homogeneous biantennary N-glycans featuring terminal α2,6-sialylation, furthermore, the introduction of new additional N-glycosylation sites via site-directed mutagenesis has significantly improved the efficacy of EPO.
Strategies of N-Linked Glycoengineering in Mammalian Cell
|
1
|
Removal of α1,3 Gal and Neu5Gc
|
Stable knockout of α1,3-galactosyltrans-ferase and CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase.
|
|
2
|
Elimination of α1,6-fucosylation
|
Disruption of FUT8 gene by target knockout;
Co-expression of GnTIII and ManII;
Expression of the inhibitor, prokaryotic RMD.
|
|
3
|
Introduction of sialylation pathway
|
Overexpression of human β1,4-GalT and α2,6-ST;
Overexpression of the CMP-sialic acid transporter;
Overexpression of the CMP-sialic acid synthase;
Inhibition of sialidase by siRNA-mediated knockdown;
Chemoenzymatic for α2,6 sialylation.
|
|
4
|
Introduction of bisecting GlcNAc
|
Overexpression of human GnTIII.
|
|
5
|
Control of glycan heterogeneity
|
Combinational knockout of GTs to produce almost homogenous biantennary N-glycans.
|
Applications of Glycoengineered Mammalian Cells
-
Production of therapeutic antibodies with enhanced ADCC, CDC, and prolonged circulation time.
-
Production of therapeutic glycoproteins, such as rhEPO, with improved efficacy and extended half-lives.
-
Enzyme replacement therapies through increased M6P to improve delivery and circulation.
Advantages of Our Services
-
Stable and functional gene knockout with minimal off-target effects
-
Site-directed and stable introduction of target genes with high expression
-
Various glycoengineering strategies for the humanization of glycoprotein products
-
Custom-designed glycosylation across various applications
Published Data
Technology: Glycoengineering in CHO cells
Journal: Nature Communications
IF: 16.6
Published: 2019
Results: Lysosomal replacement enzymes represent crucial therapeutic interventions for rare congenital lysosomal enzyme deficiencies. An extensive genetic engineering screen was conducted using CHO cells, aimed to enable the production of lysosomal enzymes with N-glycans that are custom-designed to influence critical glycan attributes, thereby enhancing cellular uptake and circulation.
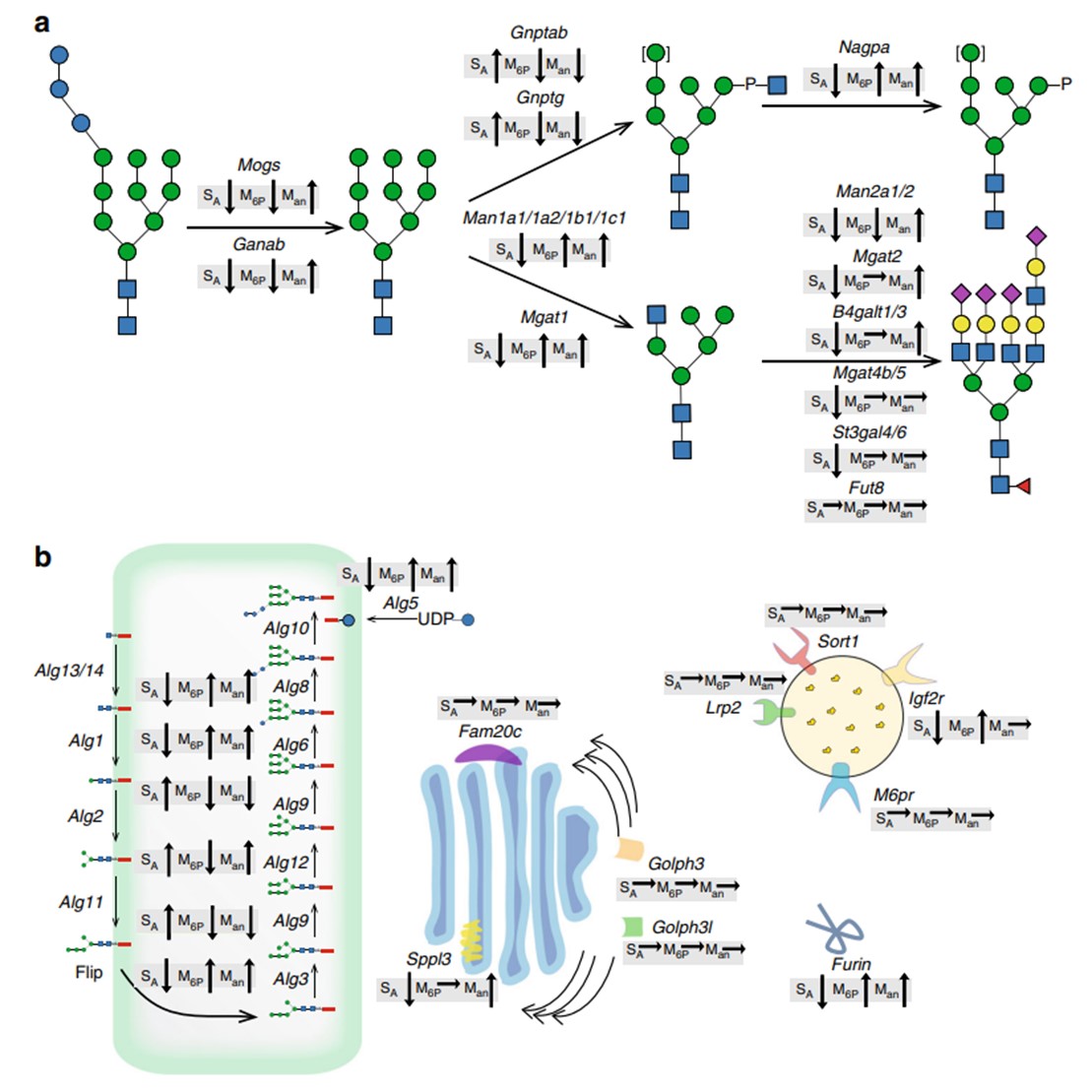 Fig.1 Trend effects of gene targeting screen on N-glycosylation of GLA.1, 2
Fig.1 Trend effects of gene targeting screen on N-glycosylation of GLA.1, 2
Glycoengineering to produce glycoprotein biologics with desired glycans is of great commercial interest. Creative Biolabs is proud to provide comprehensive N-linked glycoengineering services in mammalian cells to meet the increasing demand for diverse and highly effective biotherapeutic glycoproteins. If you have specific questions or require assistance with glycoengineering needs, please feel free to contact us for more information.
References
-
Tian, Weihua, et al. "The glycosylation design space for recombinant lysosomal replacement enzymes produced in CHO cells." Nature communications 10.1 (2019): 1785.
-
Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Trend effects of gene targeting screen on N-glycosylation of GLA.1, 2
Fig.1 Trend effects of gene targeting screen on N-glycosylation of GLA.1, 2

