What Are Glycoproteins Made of?
What Are Glycoproteins Made of?
Glycoproteins are composed of proteins that are covalently linked to carbohydrate chains (also known as glycans). These glycans are essential for the glycoprotein's stability, function, and interactions with other molecules. The carbohydrates attached to the protein backbone are highly variable, consisting of different sugar molecules such as glucose, galactose, mannose, and sialic acid, which can be linked in various configurations to form complex sugar structures. Glycoproteins play an indispensable role in numerous biological processes, including immune responses, cell signaling, and the regulation of protein stability. However, due to the complexity of their structure—comprising both proteins and carbohydrate chains—the analysis of glycoproteins presents significant challenges. These challenges arise from the heterogeneity of glycans, their low abundance in some biological systems, and the wide variety of structural modifications.
As a pioneering leader in the field, Creative Biolabs has leveraged its expertise and cutting-edge technologies to develop comprehensive glycoprotein structure analysis services. Our services are tailored to meet the needs of researchers, pharmaceutical companies, and biotechnology firms focused on glycoprotein structural characterization. By utilizing a wide range of glycoprotein analysis techniques, we help researchers uncover the intricacies of glycoprotein structure, improving their understanding of glycoprotein functional properties. With several years of experience, we take pride in offering innovative and highly reliable glycoprotein analysis solutions, ensuring our clients achieve success in their projects.
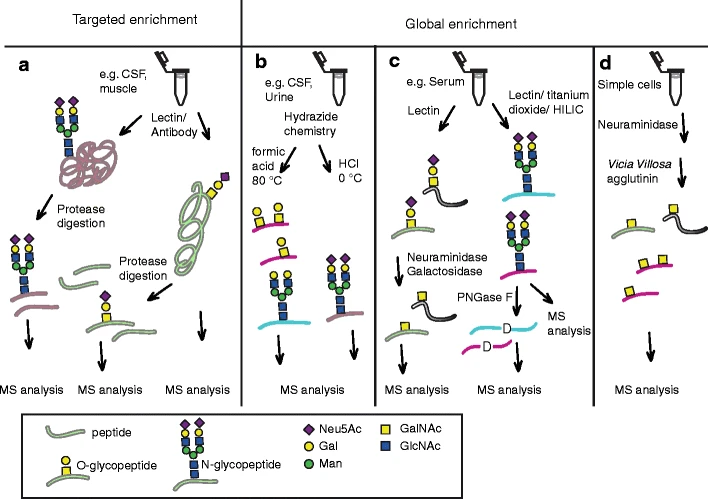 Fig.1 Schematic representation of methods for targeted and global enrichment of glycoproteins and glycopeptides.1
Fig.1 Schematic representation of methods for targeted and global enrichment of glycoproteins and glycopeptides.1
Techniques for Glycoprotein Structure Analysis
To unravel the complexity of glycoprotein structures, a range of advanced techniques is used. These glycoprotein analysis techniques allow scientists to determine the exact structure of glycoproteins, including identifying the glycosylation sites and understanding how these modifications affect protein functionality.
|
Technology
|
Technology Overview
|
Applicable Glycoprotein Types
|
Applications in Glycoprotein Analysis
|
|
Lectin Microarray
|
A high-throughput platform that uses lectins to bind specifically to certain sugar residues, enabling the profiling of glycoproteins based on their glycan structures.
|
Cell surface glycoproteins, Serum glycoproteins
|
Screening glycan structures, Mapping glycan epitopes, Glycoprotein profiling.
|
|
Mass Spectrometry (MS)
|
An analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of ions, used to identify the molecular structure of glycoproteins, including their glycan composition and glycosylation sites.
|
Therapeutic glycoproteins, Viral glycoproteins
|
Glycoprotein structure determination, Glycosylation site mapping, Identification of glycan modifications.
|
|
Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS)
|
A hybrid technique combining liquid chromatography for separation and electrospray ionization coupled with mass spectrometry to analyze glycoprotein structure and glycan composition.
|
Monoclonal antibodies, Recombinant proteins
|
Separation and analysis of glycoproteins, Glycan profiling, Quantification of glycosylation.
|
|
Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS)
|
A mass spectrometry technique that uses a laser to ionize samples, providing detailed analysis of glycoprotein structure and glycosylation patterns.
|
Antibodies, Enzymes, Viral proteins
|
Glycoprotein identification, Glycan profiling, Peptide mapping.
|
|
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
|
A chromatographic technique for separating and analyzing glycoproteins based on their size, charge, and hydrophobicity, allowing for high-resolution glycan separation.
|
Plasma proteins, Serum proteins
|
Purification of glycoproteins, Quantification and analysis of glycoproteins, Glycan analysis.
|
|
High-Performance Anion-Exchange Chromatography with Pulsed Amperometric Detection (HPAEC-PAD)
|
A chromatography technique that separates sugars in glycoproteins based on charge, using amperometric detection to quantify the sugars.
|
Monosaccharides, N- and O-linked glycans
|
Analysis of sugar composition, Detection of sugar moieties in glycoproteins, Characterization of glycan structures.
|
|
Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
|
A chromatographic method used to separate hydrophobic glycoproteins based on their affinity to a hydrophobic stationary phase.
|
Therapeutic glycoproteins, Viral glycoproteins
|
Purification and characterization of glycoproteins, Glycan analysis, Protein integrity assessment.
|
|
Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection-Quadrupole Time-of-Flight (UHPLC/FLD/Q-TOF)
|
Combines fluorescence detection with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry for ultra-sensitive detection of glycoproteins and their glycan content.
|
Complex glycoproteins, Enzyme-linked glycoproteins
|
High-sensitivity detection of glycoproteins, Characterization of glycoproteins and glycan structures, Quantitative glycoprotein analysis.
|
|
Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy for Glycan Analysis
|
A spectroscopic technique that measures the infrared absorption of glycoproteins, useful for determining glycan composition and sugar linkage types.
|
Glycoproteins with complex glycans, Membrane-bound glycoproteins
|
Glycan analysis, Sugar identification, Analysis of glycan-protein interactions.
|
|
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy for Glycan Analysis
|
A technique that provides detailed molecular-level information about glycoprotein structures, including glycan conformation and 3D structure.
|
Glycoproteins with complex glycan structures
|
Characterization of glycan linkages, Conformational analysis of glycoproteins, Analysis of glycoprotein interactions.
|
|
Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging (SPRi) for Glycoprotein Profiling
|
A powerful technique for studying protein-ligand interactions and glycoprotein profiling by measuring changes in the refractive index as glycoproteins interact with specific ligands.
|
Cell surface glycoproteins, Glycoproteins in diagnostics
|
Profiling glycoprotein interactions, Analyzing glycan-binding proteins, Quantitative interaction analysis.
|
|
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) for Glycan Analysis
|
A technique for separating and analyzing volatile compounds, used for glycan analysis by converting sugars into derivatized forms before mass spectrometry analysis.
|
Monosaccharides, Small glycan molecules
|
Glycan composition analysis, Sugar quantification, Structural identification of small glycans.
|
Features of Our Technologies
-
Specificity and veracity
-
High sensitivity
-
Stability and consistency
-
Low-cost
-
Best after-sale service
Applications of Glycoprotein Structure Analysis
Clinical Therapeutic Proteins
Glycoproteins in therapeutic proteins, such as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), growth factors, and cytokines, are critical for the success of biopharmaceuticals. The glycosylation of therapeutic proteins can impact their pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and immune response. Detailed glycoprotein structure analysis is essential for optimizing the design of recombinant therapeutic glycoproteins and ensuring their clinical success. Our glycoprotein structure analysis in biopharmaceuticals helps ensure that therapeutic proteins have the correct glycosylation patterns for maximum safety and efficacy.
Serum Proteins
Serum glycoproteins, such as erythropoietin (EPO) and α-1-acid glycoprotein (AGP), are important biomarkers in disease diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. By analyzing the glycosylation patterns of serum proteins, researchers can detect glycosylation changes associated with disease states, providing important insights for personalized medicine. Through our serum glycoprofiling services, we help identify glycosylation changes that are crucial for clinical diagnostics.
Viral Spike Proteins
Viral glycoproteins, particularly the spike proteins, are key to viral entry into host cells. The glycosylation patterns of viral glycoproteins influence their infectivity and ability to evade the host immune response. By studying these glycoproteins, researchers can gain critical insights into viral pathogenesis and the development of targeted therapies. Creative Biolabs offers glycosylation analysis services for virus glycoproteins, supporting the study of glycoproteins involved in SARS-CoV-2, HIV, and influenza.
Glycoproteins in Disease Treatment
Glycoproteins are often implicated in the pathogenesis of diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer's, and autoimmune disorders. Understanding the role of glycoproteins in disease through structure analysis is essential for identifying new biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Our customized glycoprotein analysis services support the identification of glycoproteins in disease treatment, enabling the development of novel therapies.
Vaccine Development
The glycosylation of viral glycoproteins has a significant impact on immune response and vaccine efficacy. By analyzing these glycoproteins' structure, researchers can enhance the design of vaccines and improve their effectiveness. Our glycosylation analysis services for COVID-19 glycoproteins help optimize the glycan profile of viral proteins, facilitating the development of more effective vaccines.
Glycoprotein Structure Analysis Services Facilitating Your Research
Using a combination of cutting-edge glycoprotein analysis technologies, we offer a full range of services, including glycan profiling, glycomic profiling, glycosylation site mapping, and glycan sequencing. Our tailored solutions are designed to meet the specific needs of your research with high precision.
Glycan Profiling
Glycan profiling is an innovative technique that focuses on quickly and efficiently capturing essential details about target glycans, rather than spending unnecessary time on intricate structural analysis. By using methods like capillary electrophoresis, liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), reversed-phase-high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC), and the emerging lectin microarray, we can profile glycans in a fast, sensitive, and high-throughput way.
Glycomic Profiling
Glycomic profiling can identify a wide range of N- and O-glycans in biological samples, including secretions, cell lines, tissues, and organs. This method uses high-sensitivity mass spectrometric (MS) techniques such as electrospray ionization (ESI) and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS), along with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) linkage analysis, to capture detailed information on glycan structures and their roles in biological processes.
Glycosylation Site Mapping
Mapping glycosylation sites provides valuable insight into how glycans affect protein function and structure. It can also reveal key aspects of glycoprotein activity, microheterogeneity, and its potential impact on biological outcomes. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) is widely used to map glycosylation sites across glycoproteins from various sources, such as plasma, cells, tissues, and whole organisms.
Glycan Sequencing
Glycan sequencing involves carefully releasing N- and O-glycans from glycopeptides using enzymatic or chemical methods, followed by solid-phase extraction and derivatization. This approach offers a detailed look at glycan sequences and structures, providing the essential data needed to understand their biological functions and contributions to cellular processes.
Glycoprotein structure analysis has become a regular study in glycosylation engineering, which is beneficial for the assignment of distinct functional properties to defined structural features. With decades of experience, Creative Biolabs has successfully completed a lot of therapeutic glycoprotein projects. We can offer a whole set of glycoprotein structure analysis services to help you get landmark development. We can also customize our offering to meet your specific project needs. If you are interested, please contact us without hesitation.
Published data
Glycoprotein structure analysis is essential for viral research. This study employs single-particle cryo-electron microscopy to capture the high-resolution (3.9 Å) structure of the post-fusion S2 subunit of the SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein. The results reveal significant conformational changes that occur in the S2 subunit during membrane fusion, particularly the formation of the HR1-HR2 six-helix bundle and the strong binding of the linker region. These changes are critical for the membrane fusion process. Furthermore, the findings provide crucial insights into how coronaviruses fuse with host membranes, which is essential for understanding viral entry. Additionally, the study identifies potential targets for developing broad-spectrum vaccines and therapies aimed at combating SARS-like coronaviruses. By utilizing single-particle cryo-EM, this research not only demonstrates the power of this technique in analyzing complex glycoprotein structures but also underscores its importance as an invaluable tool for advancing virology studies.
 Fig.2 Structural changes of the SARS-CoV glycoprotein from pre-fusion to post-fusion detected by cryo-EM.2
Fig.2 Structural changes of the SARS-CoV glycoprotein from pre-fusion to post-fusion detected by cryo-EM.2
FAQs
Q1: What is the purpose of glycoprotein structure analysis?
Glycoprotein structure analysis helps to uncover the detailed architecture of glycoproteins, including their glycan components. This is crucial for understanding their biological functions, interactions, and roles in diseases, and is particularly important for optimizing therapeutic proteins, vaccine development, and diagnostic tools.
Q2: What are the applications of glycoprotein structure analysis in viral research?
In viral research, glycoprotein analysis helps to examine viral spike proteins, which are key for viral entry into host cells. By studying their glycosylation patterns, researchers can gain insights into viral pathogenesis, immune evasion mechanisms, and design targeted therapies or vaccines. (Glycosylation Analysis Services for Virus Glyoprotein)
Q3: Which techniques are used to analyze glycoprotein structures?
Various advanced techniques are used, such as mass spectrometric (MS), lectin microarray, liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS), and cryo-EM. These methods enable high-resolution analysis of glycan compositions, glycosylation sites, and the impact of these modifications on protein function.
Customer Review
Accurate viral glycoprotein analysis
"Creative Biolabs' glycoprotein analysis services were instrumental in our project on viral glycoproteins. Their ability to accurately identify glycosylation sites and analyze modifications allowed us to better understand viral entry mechanisms. The results were precise, and the support was outstanding."
Excellent glycoprotein analysis for drug development
"We utilized Creative Biolabs' glycoprotein structure analysis services for our monoclonal antibody research, and we were extremely impressed. The team’s expertise in glycosylation mapping helped us optimize our protein's efficacy, and their insights were invaluable in fine-tuning our drug development process. Highly recommend!"
Reference
-
Nilsson, Jonas, et al. "Targeting the glycoproteome." Glycoconjugate journal 30 (2013): 119-136. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 2.0, without modification.
-
Fan, Xiaoyi, et al. "Cryo-EM analysis of the post-fusion structure of the SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein." Nature communications 11.1 (2020): 3618. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Resources
For Research Use Only.
 Contact Us
Follow us on
Contact Us
Follow us on

 Fig.1 Schematic representation of methods for targeted and global enrichment of glycoproteins and glycopeptides.1
Fig.1 Schematic representation of methods for targeted and global enrichment of glycoproteins and glycopeptides.1
 Fig.2 Structural changes of the SARS-CoV glycoprotein from pre-fusion to post-fusion detected by cryo-EM.2
Fig.2 Structural changes of the SARS-CoV glycoprotein from pre-fusion to post-fusion detected by cryo-EM.2

