Extractive Profiling Service
Services Published Data FAQs Customer Review
Reliable and Efficient Extractables Analysis Service at Creative Biolabs
Lignocellulose is a recyclable material resource. Creative Biolabs is a leader in life science research, development, analysis, etc. We have an experienced team of professionals and state-of-the-art equipment to analyze Lignocellulose and other Biomass samples for extractives. We have optimized the process of lignocellulosic extractives analysis to provide strong support for our clients' scientific and biomass research work.
-
Detection equipment
Solvent extractor: It is used to determine the content of extractives including water-soluble and ethanol-soluble extractives in biomass samples such as lignocellulose.
-
Detection indicator
-
Water-soluble extractive content
-
Ethanol-soluble extractive content
-
Water-insoluble but ethanol-soluble extractive content
-
Exhaustive extractive content (i.e., the total content of water-insoluble but ethanol-soluble extractives and water-soluble extractives)
-
Detection steps
-
The moisture content is determined in the sample.
-
We extract water-soluble and ethanol-soluble extractives from the sample by solvent extractor.
-
We calculate the amount of each extractive contained in the sample (water-soluble extractive, ethanol-soluble extractive, water-insoluble but ethanol-soluble extractive, and exhaustive extractive) by the mass loss in the sample caused by extraction.
Our goal is to accelerate the analysis and utilization of biomass samples such as lignocellulose by our clients. Like our Ash Content Analysis, Lignin Content Analysis, Starch Content Analysis, etc., our extractive analysis method is equally efficient and provides accurate results. We also identify and quantify the components of the extractives if the client requires further analysis.
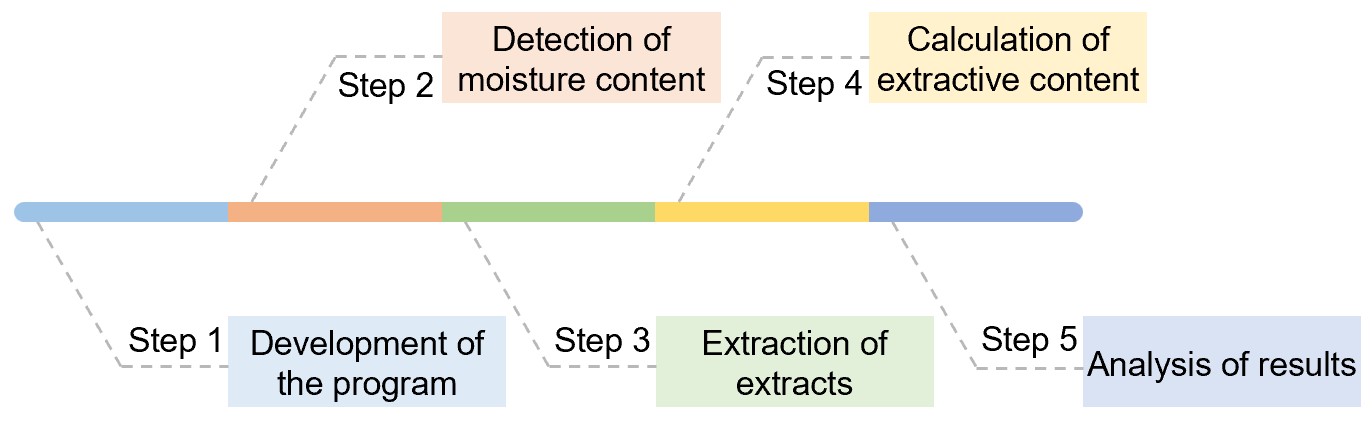 Fig.1 Flowchart for extractive analysis.
Fig.1 Flowchart for extractive analysis.
Advantages of Extractables Analysis Service
-
Professional service: Our lignocellulosic extractive analysis service is handled by professional and experienced scientists.
-
Flexible experimental program: We flexibly adjust the extractive analysis program according to the actual needs of our clients on time.
-
High accuracy: Our extractive analysis process is experimentally verified, and the results are highly precise and accurate.
Lignocellulosic and other biomass analyses are essential for understanding the quality and composition of biomass feedstocks, evaluating their suitability for specific applications, and optimizing biomass-based processes. Creative Biolabs facilitates lignocellulosic and other biomass analyses for our clients by providing specialized extractive analysis services. We help clients to interpret all the results in our analyses. Please feel free to contact us if you have any questions about extractive analysis.
Published data
Microalgae biomass is rich in various organic compounds, such as lipids, proteins, and pigments, and can be used as a source of bioactive compounds. Among them, the lipid content in microalgae is 25 to 200 times that of plants, making it an ideal choice for industrial lipid production and application. The main lipids in microalgae include phospholipids, acylglycerides, glycolipids, free fatty acids, sterols, etc. Traditional lipid extraction methods usually require dehydration of microalgae biomass before extraction, which is a process with high energy consumption and thus increases costs. Therefore, extracting lipids directly from wet biomass would be an advantageous strategy. This study discussed and introduced a variety of pretreatment technologies for extracting lipids from wet microalgae biomass, including microwave, ultrasound, bead milling, enzymolysis, hydrolysis, ionic liquids, and patented processes (such as mechanical crushing, organic extraction, etc.), and analyzed the advantages and disadvantages of various methods. Finally, the authors pointed out that in the process of wet microalgae extraction, those extraction methods that are sustainable, efficient, versatile, and controllable should be given priority.
 Fig.2 Mechanism of enzymatic cellulose degradation.1
Fig.2 Mechanism of enzymatic cellulose degradation.1
FAQ
Q1: What is the significance of extractive analysis for bioconversion and processing of lignocellulose?
A1: Biomass extractive analysis helps to assess the quality and composition of biomass such as lignocellulose. Meanwhile, extractive analysis also plays a vital role in studying the potential applications of lignocellulose and optimizing the processing.
Q2: What methods are commonly used in biomass extractive analysis?
A2: Common methods for biomass extractive analysis include solvent extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, ultrasound-assisted extraction, and so on. Each method has its advantages and needs to be selected according to the characteristics of the biomass sample and the target compounds.
Customer Review
Excellence in Extractive Analysis
"Creative Biolabs impressed us with their extractive analysis services. They used advanced technology to provide us with accurate extractive analysis results. Throughout the analysis process, their staff showed great professionalism and answered all our questions, which helped us analyze the results accurately. They truly lived up to their promise of providing exceptional service."
Customer Focused
"We always choose Creative Biolabs to help us analyze the individual components in lignocellulose. Their extractive analysis services were of very high quality. They were always customer-centered, understood our needs, and developed custom protocols. The accurate results of the extractive analysis, delivered on time, helped us to carry out the subsequent studies smoothly."
Reference
-
Pôjo, Vânia, Tânia Tavares, and Francisco Xavier Malcata. "Processing methodologies of wet microalga biomass toward oil separation: An overview." Molecules 26.3 (2021): 641. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Flowchart for extractive analysis.
Fig.1 Flowchart for extractive analysis.
 Fig.2 Mechanism of enzymatic cellulose degradation.1
Fig.2 Mechanism of enzymatic cellulose degradation.1

