Introduction of Capsular Polysaccharides (CPS)
Bacterial capsules are a vital structure shared by diverse bacteria, consisting of long polysaccharide chains called CPS, which are usually negatively charged, thus resulting in a hydrated capsular layer. CPS is present on the surface of a variety of bacteria and may be attached to the cell surface through covalent attachment to phospholipids or lipid A molecules. Moreover, a given bacterial species can produce various CPS with distinct structures, which contribute to distinguishing isolates by serotyping. Furthermore, CPS has long been recognized as a significant virulence factor for multiple pathogens.
Composition and Structure
CPS are hydrated molecules with more than 95% water. CPS are diverse molecules that differ not only in their constituent monosaccharides but also in the way they are linked. CPS consists of repeating monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds. They can be homopolymers or heteropolymers and can be replaced by organic molecules such as acetyl groups as well as inorganic molecules such as phosphate. Most bacterial capsules are made up of polysaccharides, but there are some exceptions such as poly-D-glutamate in Bacillus anthracis. It is worth noting that since most capsules are tightly packed, many stains cannot infiltrate the capsule, so they are very difficult to stain.
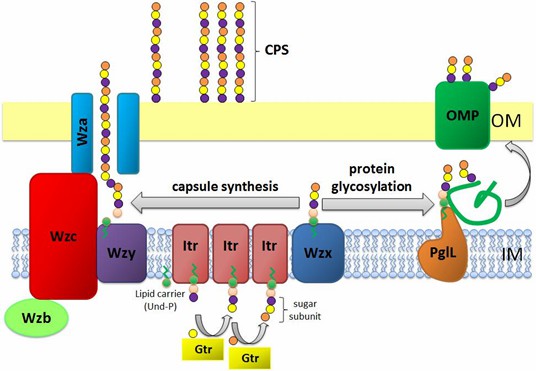 Fig.1 Schematic
representation of CPS assembly in A. baumannii. (Singh, 2019)
Fig.1 Schematic
representation of CPS assembly in A. baumannii. (Singh, 2019)
Functions
CPS represents the outermost layer of bacterial cells, thus CPS plays a crucial role in the interaction between bacteria and the environment. Bacterial CPS has many functions, including anti-desiccation, adhesion, and anti-nonspecific host immunity, all of which are directly related to pathogenicity.
Resistance to desiccation
CPS are hydrating molecules located on the surface of cells, and they are essential for protecting bacteria from the unfavorable effects of desiccation. Studies have shown that in Escherichia coli genes encoding specific biosynthetic enzymes are upregulated under desiccation conditions. In addition, CPS may be involved in the protective effect of the host-to-host transmission process. Importantly, they facilitate the exclusion of viruses and hydrophobic toxic substances such as detergents.
Adherence
CPS occupies a critical position in the adhesion between bacteria and organisms. CPS is beneficial in promoting bacterial adhesion to other bacterial cells, which contributes to promoting the colonization of specific niches and may lead to the formation of biofilms. In general, adhesion to host tissues is closely linked to a range of bacterial surface components, CPS has been implicated in the adhesion of many human pathogens to host tissues.
Resistance to host immunity
The CPS interacts with the complement system. Besides, CPS is also key components responsible for resisting host non-specific immunity. During pathogen infection, the interaction between bacterial CPSs and the immune system is a key factor in determining the fate of the infection. CPS can modulate the host immune system by stimulating the release of certain cytokines, resulting in the disruption of cell-mediated immune responses. Furthermore, CPS is believed to confer host resistance to specific immune responses.
Relying on mature technologies such as hybridoma and phage display and rich experience, Creative Biolabs is confident to provide highly specific antibodies (Abs), including but not limited to anti-capsular polysaccharide Abs and Anti-microbial lipopolysaccharide Abs. If you are interested in our Abs, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
- Singh, Jennifer K., Felise G. Adams, and Melissa H. Brown. "Diversity and function of capsular polysaccharide in Acinetobacter baumannii." Frontiers in microbiology 9 (2019): 3301. Distributed under Open Access license CC By 4.0, without modification.
-
-
AibGenesis™ Anti-C. neoformans GalXM Monoclonal Antibody (Mouse mAb) (CAT#: MAS-0524-YJ63)
- Host: Mouse
- Reactivity: C. neoformans
- Applications: ELISA; IF
- Conjugations: Conjugation could be customized
-
-
-
AibGenesis™ Anti-C. neoformans P601E Monoclonal Antibody (Human mAb) (CAT#: MAS-0524-YJ66)
- Host: Human
- Reactivity: C. neoformans
- Applications: ELISA
- Conjugations: Conjugation could be customized
-
-
-
AibGenesis™ Anti-C. neoformans GXM Monoclonal Antibody (Mouse mAb) (CAT#: MAS-0524-YJ64)
- Host: Mouse
- Reactivity: C. neoformans
- Applications: ELISA; IF; Inhib; FC; FuncS
- Conjugations: Conjugation could be customized
-
-
-
AibGenesis™ Anti-C. neoformans GXM Monoclonal Antibody (Human mAb) (CAT#: MAS-0524-YJ65)
- Host: Human
- Reactivity: C. neoformans
- Applications: ELISA; IF; Inhib; FC; FuncS
- Conjugations: Conjugation could be customized
-
For Research Use Only. Do NOT use in humans or animals.