Creative Biolabs has unique R&D expertise to provide the highest quality antibody products in the industry at different sizes and affordable prices. At the same time, we did a comprehensive analysis of the antibodies. During the development and manufacturing process, each antibody product is strictly monitored following our strict quality assurance and quality control standards.
Overview
Proteins can also localize as polymeric assemblies inside the cell. These assemblies are called cytoskeletal elements.
- The eukaryotic cytoskeleton includes both stable filamentous structures that are composed largely of intermediate filament proteins and dynamic structures such as tubulin-derived microtubule structures and actin filaments that can be rapidly assembled, disassembled, and redistributed within the cell in response to signals that regulate cell function, such as cell cycle progression, intracellular organelle transport, motility, and cell shape.
- The cytoskeleton structure of bacteria, a filamentous structure based primarily on a polymer class of proteins, exhibits a long range of order within the cell, and this has been studied, that are capable of self-assembling in vitro into extended polymeric filaments. The cytoskeleton of bacteria consists of several sets of intracellular structures that fit this definition
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cytoskeletal Elements
- Properties and Functional Relationships
Prokaryotic cells contain homologs for each of the three major groups of eukaryotic cytoskeletal proteins, i.e., actin, tubulin, and intermediate filament proteins. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cytoskeletal proteins also have two important properties. First, they self-assemble into filamentous polymers in vitro in the presence of ATP (most proteins) or GTP (tubulin and tubulin homologies). Second, they are organized into ordered, long-range structures within the cell.
- Membrane-Associated Cytoskeletal Structures
In eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, many cytoskeletal structures are associated with membrane surfaces. Primary filamentous cytoskeletal proteins can interact directly with the lipid bilayer via a specialized membrane-binding domain. An important role of the submembrane cytoskeleton network of eukaryotic cells is to provide a framework for communication between the cell-outside world through protein complexes that include transmembrane elements. In bacterial cells, the MreB/MreC/PBP transmembrane complex appears to perform a similar role by connecting the MreBC cytoskeleton to the myelin layer of the cell envelope and regulating its biogenesis.
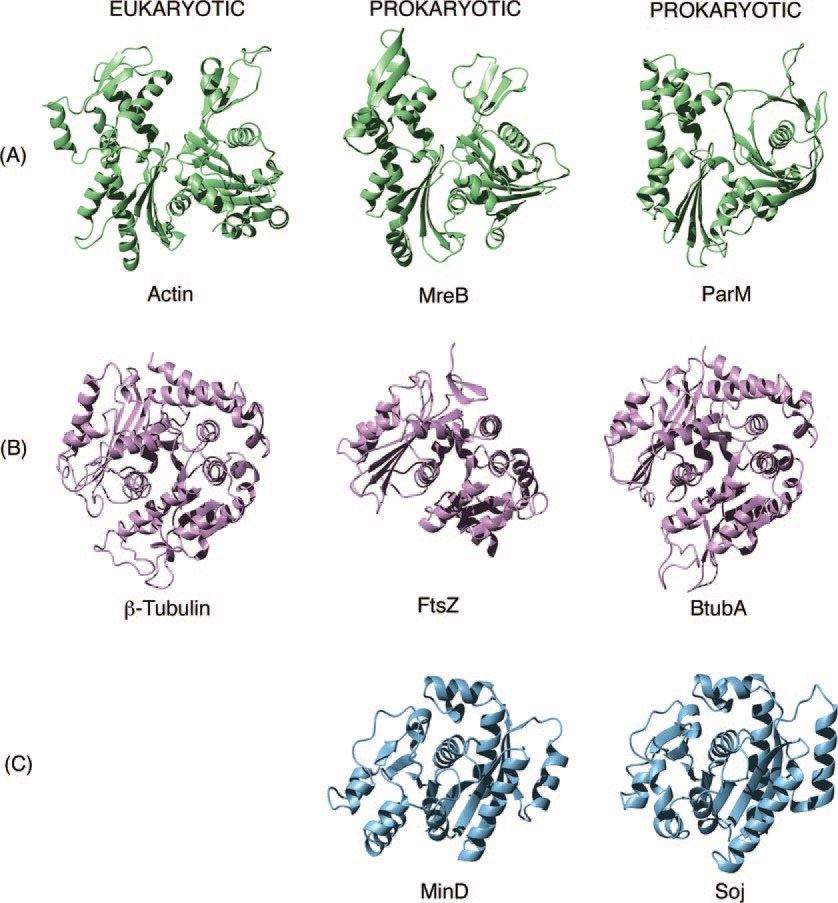 Fig.1 Schematic diagram showing bacterial cell communication mediated by surface appendages and cytoskeleton proteins.1
Fig.1 Schematic diagram showing bacterial cell communication mediated by surface appendages and cytoskeleton proteins.1
Related Anti-Microbial Protein Antibody Products
Creative Biolabs is one of the nation's leading suppliers of flexible and specialized contract development of high-quality antibodies, including monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, to pharmaceutical, bioscience, and contract research organizations. We have been chosen by our large pharmaceutical and biotech customers because we minimize your risk and time and save your resources. If you would like to know more details about our antibody products or would like to consult our experts, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
- Singhi, Divya, and Preeti Srivastava. "Role of bacterial cytoskeleton and other apparatuses in cell communication." Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences 7 (2020): 158. Distributed under Open Access license CC By 4.0, without modification.
-
-
Anti-S. aureus FtsZ Antibody (Rabbit pAb) (CAT#: MAS-0524-YJ28)
- Host: Rabbit
- Reactivity: S. aureus
- Applications: ELISA; WB
- Conjugations: Unconjugated
-
-
-
Anti-E. coli mreB Antibody (Rabbit pAb) (CAT#: MAS-0524-YJ27)
- Host: Rabbit
- Reactivity: E. coli
- Applications: ELISA; WB
- Conjugations: Unconjugated
-
For Research Use Only. Do NOT use in humans or animals.