Rickettsiae is a group of small, pleomorphic bacteria that may exist in cocci, bacilli, or thread-like forms. Typical Rickettsiae have an analogous structure to Gram-negative bacteria (GNB). The typical envelope contains three crucial layers: an inner cytoplasmic membrane, the cell wall as well as the outer layer. Importantly, the chemical composition of the outer layer is similar to that of typical membranes and that the cell wall is chemically similar to GNB. It is worth mentioning that Rickettsiae have a typical bacterial cell wall but no flagella. In general, Rickettsiae occur alone, in pairs, or in clusters. Most species exist only in the cytoplasm of the host cell, but species related to spotted fever reproduce in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Metabolism and Culture
Rickettsiae are a diverse collection of bacteria, a general characteristic of this group is that arthropods and mammals serve as their natural hosts. Rickettsia can be transmitted to humans through the bite of ticks, fleas, mites, or lice. Rickettsia spreads through the bloodstream to infect endothelial cells by a small skin portal. Rickettsiae enter their target cells, multiply by binary fission in the cytosol, and directly destroy the parasitized cell. As intracellular pathogens, Rickettsiae cannot be grown in artificial vegetative cultures, they must be grown in tissue or embryonic cultures, such as embryonated eggs.
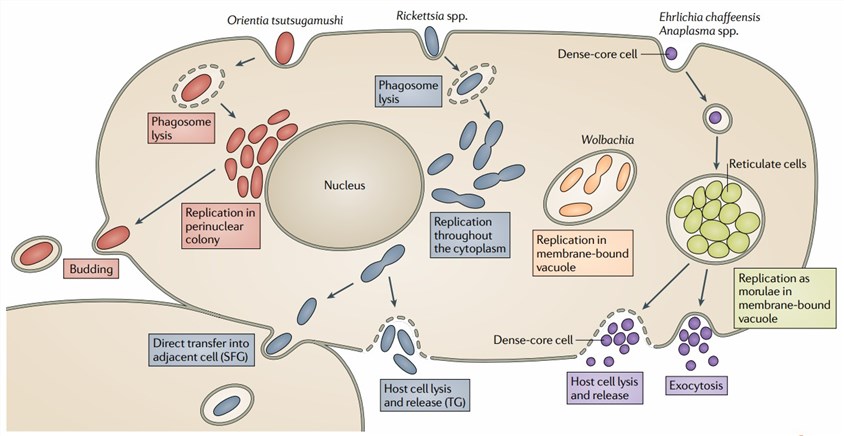 Fig.1 Rickettsia rickettsii. Distributed under Public Domain, from Wiki.
Fig.1 Rickettsia rickettsii. Distributed under Public Domain, from Wiki.
Rickettsioses and Disease
Rickettsiae are global pathogens with epidemics exacerbated by poor sanitation. Rickettsial diseases are closely linked to infections caused by bacterial pathogens belonging to the rickettsia genus. Pathogens cause disease by damaging blood vessels in various tissues and organs. Rickettsiae are closely associated with a variety of diseases, including rickettsial varicella, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, epidemic typhus, and murine typhus. The severity of the rickettsial disease varies widely, from self-limiting mild disease to life-threatening severe infection, especially if complications develop. In severe cases, multiple tissues and organs are damaged to varying degrees. Some patients present with febrile rash and visceral involvement, and symptoms may include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, hypotension, encephalitis, acute renal failure, and respiratory distress.
Diagnosis of Rickettsioses
The identification and diagnosis of Rickettsioses are challenging because the available methods come with several shortcomings. Molecular methods allow species-specific identification with rapid turnaround times. However, usage is limited in some places due to resource requirements. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) and metagenomics are emerging as hot spots for Rickettsia spp diagnosis, but genomic approaches are currently limited to laboratory studies. Importantly, the detection of antibodies (Abs) against Rickettsia is also a common approach.
If you are interested in our anti-Rickettsia Abs, please feel free to contact us.
For more Ab products, please click the link below:
-
-
Anti-R. conorii ompA Antibody (Rabbit pAb) (CAT#: MAS-0524-YJ23)
- Host: Rabbit
- Reactivity: R. conorii
- Applications: ELISA; WB
- Conjugations: Unconjugated; HRP; FITC; Biotin
-
-
-
Anti-R. japonica omp Antibody (Rabbit pAb) (CAT#: MAS-0524-YJ24)
- Host: Rabbit
- Reactivity: R. japonica
- Applications: ELISA; WB
- Conjugations: Unconjugated; HRP; FITC; Biotin
-
For Research Use Only. Do NOT use in humans or animals.