As a leading CRO of antibody generation and development, Creative Biolabs offers application-specific antibody development services to global clients. With experienced scientists and advanced technology, we have established a series of high-quality in vitro diagnostic (IVD) antibody development services against biomarkers of different diseases. Here, we introduce our IVD antibody development services for urinary 8-OHdG.
Introduction of 8-OHdG
As part of the metabolic processes and biochemical reactions, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are continuously produced in living cells of aerobionts. The reactive nature of ROS and oxygen-free radicals can result in oxidative damage to lipids of cellular DNA, proteins, and membranes, though they have important physiological functions. When an imbalance occurs, oxidants will cause extensive oxidative damage to DNA, which, in turn, contributes to aging, degenerative diseases, and malignant tumors.
Urinary 8-hydroxy-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), also referred to 8-Hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine or 8-OH-deoxyguanosine, a major DNA base-modified products, is one of the most abundant lesions in DNA. It is induced by either singlet oxygen, hydroxyl radical or photodynamic action. This oxidatively modified lesion is supported by a loss of base-pairing specificity or misreading of adjacent pyrimidines. Its pairing with adenine (A) and cytosine (C) is found to have mutagenic potential, which leads to G:C to T:A transversion mutations on DNA replications.
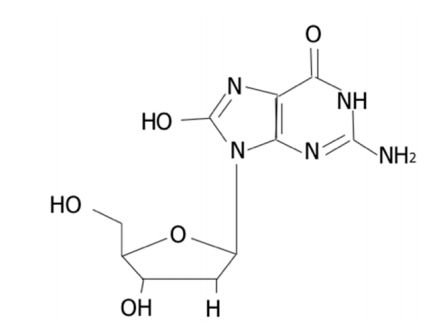 Fig.1 Structure of 8-OHdG.1, 3
Fig.1 Structure of 8-OHdG.1, 3
Measurements of 8-OHdG can be performed in animal samples, including urine, leukocyte DNA, human organs, and so on. In nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, 8-OHdG and 8-oxodG (8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2-deoxyguanosine) is relatively easily formed and pro-mutagenic, and therefore has been widely used as a biomarker of aging, oxidative stress, and carcinogenesis. Studies revealed urinary 8-OHdG is also a great marker for risk assessment of many cancers and degenerative diseases.
8-OHdG and Diseases
ROS can attack guanine (G) bases in DNA and form 8-OHdG, which can bind to thymidine (T) rather than cytosine. Based on it, the level of 8-OHdG is commonly considered a biomarker of mutagenesis consequent to the reaction of oxidative stress. For instance, higher levels of 8-OHdG have been detected in Helicobacter pylon-associated chronic atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer. Whereas, exogenous 8-OHdG is reported to paradoxically reduce ROS production, attenuate the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway, as well as moderate the expression of proinflammatory mediators. In addition, other studies have concluded that based on 8-OHdG determination, cancer tissues in humans such as renal, lung, and colorectal tumors display higher degrees of DNA oxidation compared to their nontumorous counterparts.
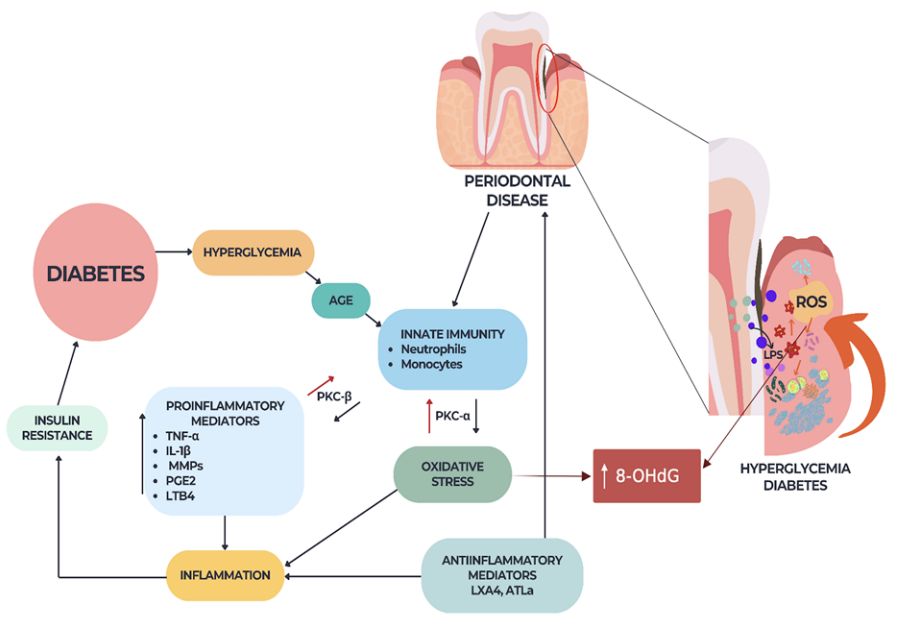 Fig.2 Periodontal disease–diabetes–ROS interrelation.2, 3
Fig.2 Periodontal disease–diabetes–ROS interrelation.2, 3
8-OHdG and Sepsis
Multiple organ failures in severe sepsis result in a prominent morbidity and mortality in patients of intensive care units (ICU). The kidney among the main injured organs is independently associated with death incidents. Acute kidney injury (AKI) and renal dysfunction occur during sepsis, together with many other confounding insults, involving ischemia-reperfusion, nephrotoxic agent, and other causes of oxidative stress.
 Fig.3 a, b, and c: Immunohistochemistry, brown staining, for 8-0H8dG in kidney before (a), 24 hrs (b) and 48 hrs (c) after S. aureus peritoneal sepsis in mice. (Bartz, R.R., 2014)
Fig.3 a, b, and c: Immunohistochemistry, brown staining, for 8-0H8dG in kidney before (a), 24 hrs (b) and 48 hrs (c) after S. aureus peritoneal sepsis in mice. (Bartz, R.R., 2014)
A connection between intracellular ROS and high levels of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage is discovered when antioxidant proteins do not adequately respond or enzymes removing the mtDNA-damaged nucleotides are invalid or overwhelmed. 8-OHdG, as a widely studied oxidative mtDNA product, is incorporated into mtDNA leading to base-pairs transversion and ineffective transcription. Nevertheless, 8-OHdG products can be repaired effectively by the enzyme named 8-hydroxyguanine DNA glycosylase (OGG1), a glycase important in DNA repair. OGG1 is previously found to play a crucial role in mtDNA 8-OHdG removal of the liver during sepsis and related its gene transcription to the regulation of nuclear genes required for mitochondrial biogenesis.
Through our role as a leading antibody service provider, Creative Biolabs is well-positioned to develop high-quality 8-OHdG-specific antibodies. Besides antibody generation, Creative Biolabs also offers diagnostic immunoassay development services, including feasibility analysis, assay design, assay protocol establishment, assay optimization, and kit production. If you are interested in our services, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
References
- Graille, Melanie, et al. "Urinary 8-OHdG as a biomarker for oxidative stress: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis." International journal of molecular sciences 21.11 (2020): 3743.
- Goriuc, Ancuta, et al. "Using 8-Hydroxy-2′-Deoxiguanosine (8-OHdG) as a Reliable Biomarker for Assessing Periodontal Disease Associated with Diabetes." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.3 (2024): 1425.
- Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.

