Concanavalin A-binding Glycoproteins Profiling
Concanavalin A (Con A) is a carbohydrate-binding protein that binding to the mannose residues of various glycoproteins, which can be extensively applied for diverse investigations. With Ph.D. level scientists and cutting-edge technology platforms in glycoprotein-related research, Creative Biolabs is able to offer the first-rate services on Con A glycoproteins profiling with perfect strategies and competitive quote.
What Is Con A?
 Fig.1 Structure of Con A. Distributed under public domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.1 Structure of Con A. Distributed under public domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Con A, a member of the legume lectin family, is a plant lectin that extracted from jack beans. It can bind to the mannose residues of various glycoproteins and stimulate lymphocytes. ConA is a commercial lectin that widely used in biology and biochemistry to characterize glycoproteins, as well as used as lectin affinity chromatography to purify glycosylated macromolecules. ConA is molecular with diverse biological activities:
-
As a lectin, ConA can interact with a wide range of receptors containing mannose carbohydrates, particularly rhodopsin, blood group markers, insulin-receptor, the immunoglobulins, and the carcino-embryonary antigen.
-
As a plant mitogen, ConA directly stimulates mouse T-cell subsets and induces several T cell populations increase.
-
ConA shows the potential therapeutic effect of against experimental hepatoma.
-
ConA-glycoenzyme couplings have proved to be a useful method in glycoenzymes solid-phase immobilization, especially those difficult to immobilize by traditional covalent coupling.
Con A-Binding Glycoproteins Profiling
As a plant lectin, Con A was reported that the widely used model for acute immune-mediated hepatitis in mice, which was driven by the activation and recruitment of T cells to the liver. However, Con A was also demonstrated to be effective on anti-hepatoma due to its autophagic cytotoxicity and immunomodulation dual properties via the specific carbohydrate binding. Con A binding glycoproteins may serve as male infertility marker proteins human seminal plasma.
Due to its significantly biological activities and diverse applications, profiles of ConA-binding glycoproteins based on modern biological technology have been well performed. Creative Biolabs has rich experience in Con A-binding glycoproteins profiling. Based on our powerful Technologies, we can offer our clients high-quality service in glycoproteins profiling.
 Fig.2 Con A-bound serum glycoproteins digested with trypsin prior to MALDI-TOF.1,3
Fig.2 Con A-bound serum glycoproteins digested with trypsin prior to MALDI-TOF.1,3
Creative Biolabs is more than happy to share our extensive experience in glycoproteins profiling. If you are interested in our glycoproteins profiling service, please feel free to contact us for more detailed information.
Published data
Glycosylation is an important post-protein modification that is widely present in organisms and is essential for maintaining normal cell functions and regulating a variety of physiological processes. Abnormal glycosylation causes changes in protein functions and stability, which is influenced by the development of various diseases. Liver fibrosis and cirrhosis are typical manifestations of a variety of chronic liver diseases, among which the activation and phenotypic transformation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) play a central role in the occurrence of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Studies have shown that after activation by transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), the abundance of ConA-recognized glycoproteins in HSCs increases; however, little is known about ConA-binding glycoproteins (CBGs) of HSCs. Therefore, in this study, the authors used targeted glycoproteomics analysis methods to compare the CBG profiles of HSCs before and after TGF-β1 activation by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with lectin-magnetic particle conjugates, aiming to discover new CBGs and determine their potential roles. The results showed that 54 and 77 proteins were identified in quiescent and activated HSC cells, respectively, of which 73.3% were new potential glycoproteins. Collectively, these findings are expected to aid future studies in uncovering the molecular mechanisms involved in HSC activation and targets for anti-fibrotic treatments.
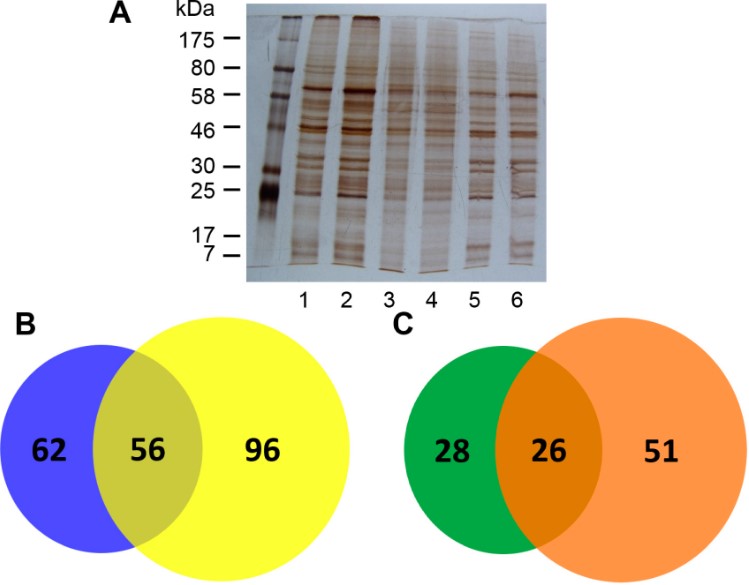 Fig.3 SDS-PAGE and MS analysis of CBG.2,3
Fig.3 SDS-PAGE and MS analysis of CBG.2,3
FAQs
Q1: How does Con A compare to other lectins in terms of binding specificity and applications?
A1: Con A is unique among lectins because it is specific for terminal α-D-mannosyl and α-D-glucosyl residues. Compared to other lectins that bind N-acetylglucosamine and sialic acid, Con A is better suited for analyzing glycoproteins rich in mannose residues. Its applications are particularly useful in studying immune responses, glycoprotein structure-functions relationships, and glycoprotein purification by lectin affinity chromatography.
Q2: What types of samples can be profiled using Con A binding glycoprotein analysis?
A2: We analyze a variety of biological types of samples using Con A binding glycoproteins. Examples include animal serum or plasma, tissue lysates, cell culture supernatants, and other body fluids (such as urine), etc. We adapt our protocols to specific sample types to ensure optimal binding and analysis results.
Customer Review
Supporting Clients' Glycosylation Research
"We found Creative Biolabs's Con A analysis service to be very valuable for our insulin receptor glycosylation research, providing clear data to support our hypothesis about receptor-ligand interactions."
Identifying New Biomarkers
"Creative Biolabs's Con A-bound glycoprotein analysis service helped us identify new biomarkers for blood group antigens, greatly advancing our hematology research. The analysis process was efficient and reliable, highly recommended, and we look forward to continued cooperation in the future."
References
-
Drake, Richard R., et al. "Lectin capture strategies combined with mass spectrometry for the discovery of serum glycoprotein biomarkers." Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 5.10 (2006): 1957-1967.
-
Qin, Yannan, et al. "Profiling of concanavalin A-binding glycoproteins in human hepatic stellate cells activated with transforming growth factor-β1." Molecules 19.12 (2014): 19845-19867.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 Structure of Con A.
Fig.1 Structure of Con A.  Fig.2 Con A-bound serum glycoproteins digested with trypsin prior to MALDI-TOF.1,3
Fig.2 Con A-bound serum glycoproteins digested with trypsin prior to MALDI-TOF.1,3
 Fig.3 SDS-PAGE and MS analysis of CBG.2,3
Fig.3 SDS-PAGE and MS analysis of CBG.2,3



